

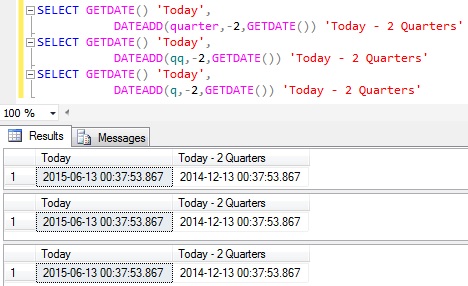
(1 row) Redshift Convert YYYYMMDD to date format:īelow example demonstrate conversion of date value from ‘YYYYMMDD’ format to date format: (1 row) Redshift Date Format Conversion ExamplesĬonvert Redshift timestamp to YYYYMMDD format: Below example demonstrate conversion of date value to ‘YYYYMMDD’ format using to_char and to_date function: training=# select TO_CHAR(TO_DATE( ' 22:30:58','YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS'),'YYYYMMDD') (1 row) Convert a String to timestamp format using TO_TIMESTAMP() Functionīelow is the example to use Redshift TO_TIMESTAMP function to convert string having date time to Redshift timestamp format: training=# Select to_timestamp('', 'DD Mon YYYY') Commonly used Amazon Redshift Date Functions and ExamplesĬonvert a String to Date format using TO_DATE() Functionīelow is the example to use Redshift TO_DATE function to convert string having date to date format: training=# Select TO_DATE( ' 23:45:58','YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS').Redshift NVL and NVL2 Functions with Examples.Different Redshift Join Types and Examples.You can use the Redshift date format functions to convert the string literals, integer, date/time etc to required format. You can directly convert the format by specifying the cast operator ( ‘::’) such as ::date, ::time, ::timestamp after the date string literal.
#REDSHIFT DATEADD ISO#
Amazon Redshift accepts different date formats, including ISO date time strings. Redshift can convert quoted date strings values to datetime data type.
The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly.

Note, you have to specify the datepart without quotes as listed in the syntax column. The table below lists the most commonly used datepart formats for the Redshift datediff function. The difference in dates returned depends on the value provided to datepart as shown below. Rather, it returns the difference between the dates specified by datepart.įor example, if date1 equals 2022-July-04 and date2 equals 2021-July-04, you would expect a difference of one year when you use the datediff function. Redshift datediff does not return the cumulative difference between two dates.If you do not care for the signed part, then use the absolute value function (abs).Similarly, if the first date is greater than the second date you get a positive number.If the first date is less than the second date, the result will be a negative number.The below 4 points are important if you want to use the Redshift datediff function correctly. What it does: The Redshift datediff function returns the difference between two dates ( date1 and date2) in the format specified by datepart. Syntax: datediff ( datepart, date1, date2) The first ( datepart) is an argument, while the second(date_part) is a date function in Redshift. You can also get the complete date part list from the Redshift documentation.Īnother point to clarify, Redshift datepart is not the same as date_part. They were chosen for being intuitive and unique to remember. The values listed are not the complete list. The table below lists the different date parts and values in alphabetic order. The value for the datepart argument is specified without quotes and in lowercase. This could be day, month, year and so on. It is a single lowercase word ( datepart) used to denote a part of a date. So, let’s clear things up.ĭate part is an argument used in Redshift date functions. Though simple, its syntax and usage can get confusing. You will see datepart mentioned in more than a few Redshift date functions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
