
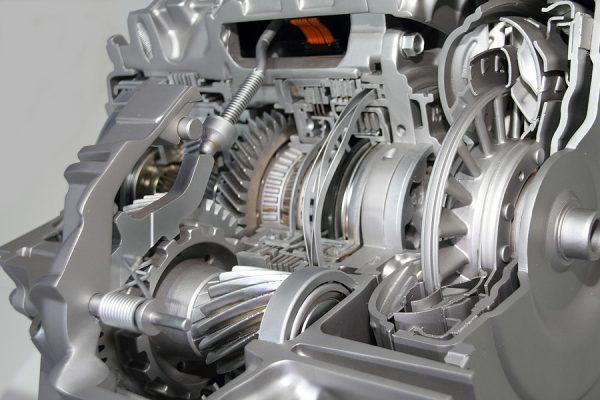
The metal belt connecting the pulleys is often referred to as the push belt as it works in compression, not tension. The variable distance between the pulley surfaces thus continuously varies the ratio between engine and vehicle speed according to driving conditions. Movement of the cylinder increases or decreases the amount of space between the two sides of the pulley, forcing the belt to ride lower or higher along the pulley walls, changing its pitch radius and, in turn, the transmission “gear” ratio.

One side of each pulley is fixed and the other side is movable, actuated by a hydraulic cylinder. A metallic belt runs in the V-groove between the two conical surfaces of each pulley, transmitting drive from the input to the output shaft. Each pulley is split down its centreline and comprises two conical surfaces facing each other, forming a V-shaped groove between them with an included angle of approximately 20 degrees. In a CVT, each of the driving (input) and driven (output) shafts have a pulley splined onto it. More than 70% of the CVTs currently produced hail from Japan’s leading manufacturers unsurprisingly, it is these manufacturers that offer CVTs on many of their models in SA. They are recognised as a more cost-effective, compact and efficient alternative to traditional torque converter automatics and their characteristics are considered particularly well matched to small- and medium-sized vehicles with petrol engines developing up to but no more than 350-400 N.m. CVTs enjoy a market share of more than 50% in Japan and are also popular in other Asian countries, as well as the US. More significant has been the increased popularity of the continuously variable transmission or CVT, now found in 17,5% of the world’s car park and outranking the dual-clutch transmission, which holds approximately 14% share. Generally speaking, the more gears in a transmission, the easier it is to maintain the optimum engine speed in different driving conditions, thus improving efficiency and fuel economy.

The most obvious change has been the trend to more gears with eight, nine and even 10 speeds becoming common.
#REVIEWS ON CVT TRANSMISSION MANUAL#
As a result, the most popular transmission types – the torque converter automatic with 37% share worldwide and the conventional manual transmission with approximately 23% share – have seen significant improvements to better match the characteristics of improved engines. However, without an appropriate transmission – carefully matched to the characteristics of the engine and thus allowing it to operate at optimum speeds and engine loads – the improved efficiencies promised cannot be realised.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
